Diabetes, also known as Diabetes mellitus is a disease that is increasing at an alarming rate. In the United States alone, according to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control), cases of diabetes have risen to an estimated 34.2 million. This was found on the National Diabetes Statistics Report for 2020. With numbers like these, one has to wonder, what is diabetes about? This article is all about diabetes.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition is initiated by the body’s lack of ability to create or
effectively use its insulin, which is produced by islet (specialized) cells found in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that assists to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels that provide energy to the body’s cells and tissues. Its function is to open cells to receive sugar from the blood. Without insulin, the cells cannot open allowing sugar to remain in the blood, elevating blood sugar levels. Additionally, without insulin the cells of the body would be starved, causing dehydration and destruction of body tissues.
Since the cells in the pancreas have been damaged in this instance, insufficient amounts or no insulin is produced causing sugar to build up in the blood.
The body needs sugar, but the sugar should not be in the blood but in cells to combine with oxygen to produce the energy that is required by the body.
Types of Diabetes
There are some different types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. It occurs when the immune system strikes and destroys cells in the pancreas, which is where insulin is produced. It is uncertain as to what is the cause of this attack. About 10% of individuals with diabetes have this type.
Type 2 diabetes happens when the body becomes opposed to insulin. The body produces enough insulin but the body seems resistant to it. This leads to a sugar build-up in the blood. This is the most common type of diabetes.
Prediabetes is a condition that happens when the blood sugar is elevated or higher than normal, but it is not high enough for a full diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes occurs when there is high blood sugar during pregnancy. Insulin-blocking hormones formed by the placenta are the cause of this type of diabetes. In addition to the placenta hormone, the stress hormone cortisol can stop insulin from working.
What is the Cause of Diabetes
Several causes are linked with each type of diabetes.
Type 1 – Health care professionals do not know precisely what causes type 1 diabetes. For some basis, the immune system erroneously damages and eliminates insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Genes can contribute a role in some individuals. An individual is more likely to get type 1 diabetes if he or she is a child or teenager, they have a parent or sibling with the condition, or they carry certain genes that are linked to the disease.
It is additionally probable that a virus engages the immune system to attack.
Type 2 – Type 2 diabetes results from a combination of genetics and behavior factors. To be overweight or obese increases the risk also. Possessing extra weight, especially in the abdominal area, causes the cells to be more resistant to the effects of insulin on blood sugar.
This type can run in families. Family members share the genes that make them more prone to get type 2 diabetes and to be overweight (more on this to follow).
An individual’s risk for type 2 diabetes increases if he or she:
- is age 45 or older
- are overweight
- are not physically active
- have a parent or sibling with the diabetes
- have an African American, Hispanic or Latino American, Alaska Native, Pacific Islander, American Indian, or Asian American ancestry
- have had gestational diabetes in the past
- have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or high triglycerides
- have prediabetes
Gestational diabetes – Gestational diabetes is the consequence of hormonal changes throughout pregnancy. The placenta creates hormones that cause an expectant female’s cells to be less sensitive to the effects of insulin. This may cause high blood sugar during pregnancy.
Individuals risk for gestational diabetes increases if they:
- are overweight
- are over age 25
- had gestational diabetes during a past pregnancy
- have a family record of type 2 diabetes
- have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Women who increase their weight too much during pregnancy are more likely to acquire gestational diabetes.
Women who acquire gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk for acquiring type 2 diabetes later on in life. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), women that give birth to a baby that weighs in excess of nine-pounds are additionally at greater risk.
Both genes and environmental components contribute a role in activating diabetes.
We often focus on sugar as the cause but sugar is not the only issue. When individuals consume carbohydrates such as potatoes, pasta, donuts, and bananas, they are broken down by enzymes into glucose (sugar). From there it enters the bloodstream and the pancreas produces insulin, which opens the cells that allow the glucose to enter the cells.
Genes and Family History – Genetics play a role in determining how likely an individual will develop some type of diabetes. Researchers do not completely understand the contribution of genetics regarding the development of diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, statistics show that if an individual has a parent or sibling with diabetes, the odds of he or she developing themselves increases.
Although research is not irrefutable, a number of ethnic groups seem to have a higher rate of diabetes. This is true for:
- African-Americans
- Asians
- Hispanic Americans
- Native Americans
- Pacific Islanders
Genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis and hemochromatosis can both damage the pancreas paving the way to a higher probability of developing diabetes.
Monogenic forms of diabetes are the result of single-gene mutations. Monogenic forms of diabetes are rare as they account for only 1 to 5% of all cases of diabetes discovered in young individuals.
An individual’s family, preexisting medical conditions, and environment can all affect the odds of developing diabetes.
Complications of Diabetes
High blood sugar affects the entire human body as it damages organs and
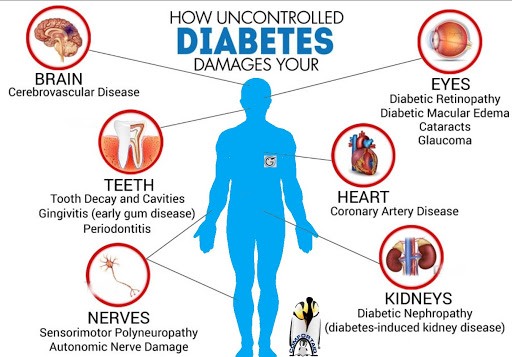
tissues throughout. The higher the blood sugar is and the longer it exists, the greater the risk for complications.
Complications associated with diabetes include:
- Heart disease, heart attack, and stroke
- Neuropathy
- Vision loss retinopathy and
- Hearing loss
- Damage to feet such as infections and sores that won’t heal
- Skin conditions like bacterial and fungal infections
- Depression
- Dementia
Additionally, unrestrained gestational diabetes can lead to problems that affect both the mother and the fetus. Complications affecting the fetus can include:
- Premature birth
- Higher than normal birth weight
- Low blood sugar
- Jaundice
- stillbirth
The mother can also develop complications such as high blood pressure (preeclampsia) or type 2 diabetes. The mother may also require a C-section also known as a cesarean delivery.
The mother’s risk of gestational diabetes in future pregnancies additionally increases.
Diabetes can progress to serious medical complications, but the condition can be managed with medications and lifestyle changes. The most common diabetes complications can be managed with the helpful tips that follow.
Symptoms of Diabetes
- Increased thirst—due to the excess of sugar in the blood, the body releases water from the cells to dilute it. This causes dehydration of the cells causing the body to desire increased water.
- Frequent urination—due to the excess sugar, the body attempts to rid itself
 of the sugar through urination. This causes an individual to become more dehydrated resulting in even more thirst.
of the sugar through urination. This causes an individual to become more dehydrated resulting in even more thirst. - Hunger—since the cells are not receiving the sugar they need to make energy, they signal for food to obtain the energy they need.
- Fatigue—the body does not have the energy it needs because of the malfunctioning cells.
- Blurred vision—this is the result of damage to the arteries at the back of the eyes. It is not necessarily permanent.
In some cases, there may be no symptoms (especially pre-diabetes and gestational diabetes).
Treatments of Diabetes
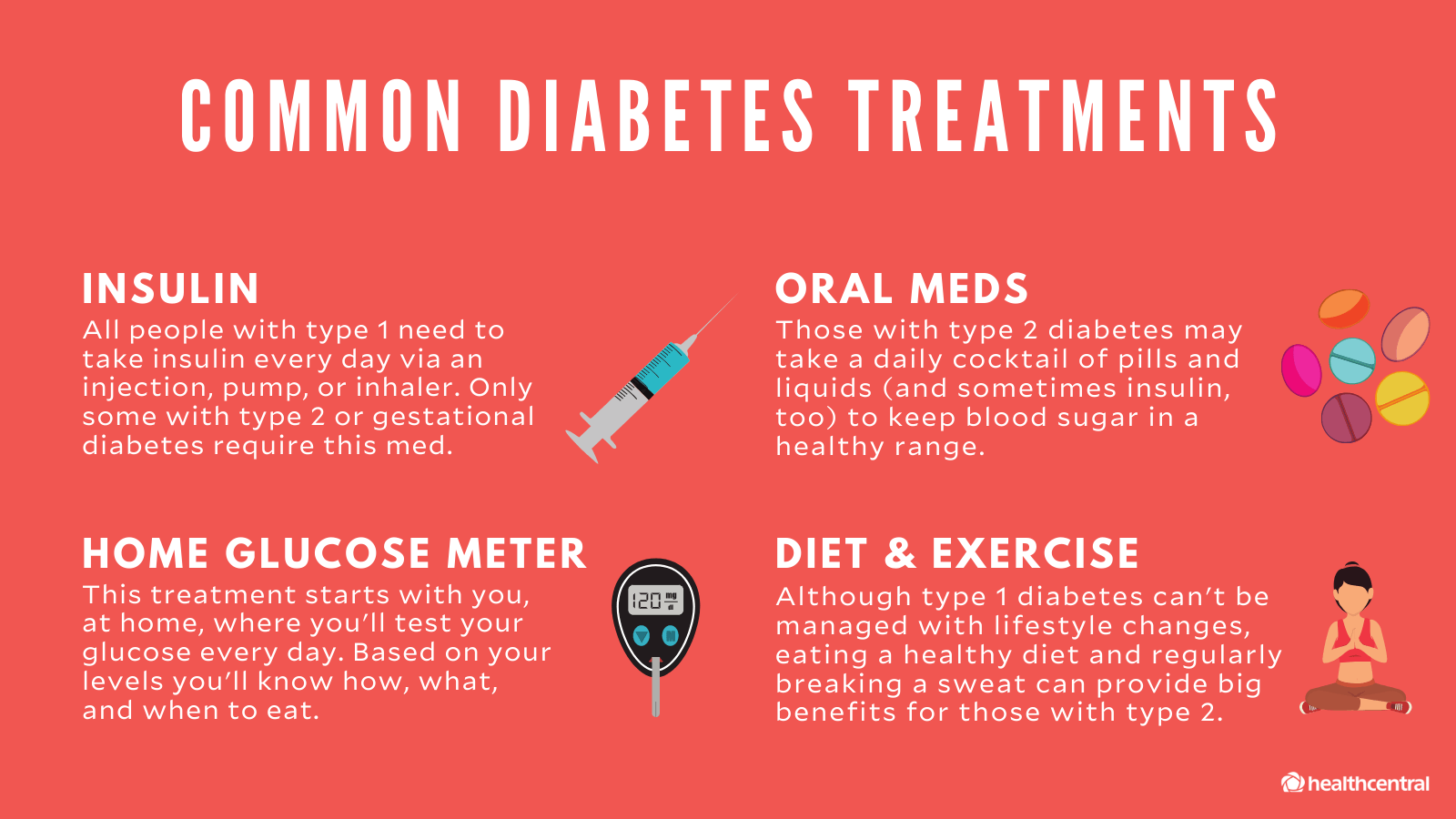
Physicians treat diabetes with a small number of various medications. Some are taken by mouth, others are available as injections.
Type 1 diabetes – Insulin is the central treatment for type 1 diabetes. It replaces the hormone that the body is not able to produce.
Four types of insulin are most commonly used. They are distinguished by how rapidly they begin to work, and how long their effects last:
- – Rapid-acting insulin begins to work inside15 minutes and its results last for 3 to 4 hours.
- – Short-acting insulin begins to work inside 30 minutes and lasts 6 to 8 hours.
- – Intermediate-acting insulin starts to work inside 1 to 2 hours and lasts 12 to 18 hours.
- – Long-acting insulin begins to work several hours after injection and lasts 24 hours or longer.
Type 2 Diabetes – Diet and exercise can assist some individuals to manage their type 2 diabetes. If lifestyle changes are not enough to lower their blood sugar, they will need to take medication.
Gestational diabetes – An individual with this condition will need to monitor their blood level several times a day during the pregnancy. If it is high, nutritional changes and exercise may or may not be sufficient enough to bring it down.
According to the Mayo Clinic, approximately 10 to 20% of females with gestational diabetes will require insulin to decrease their blood sugar levels. Additionally, insulin is safe for the growing fetus.
The drug or combination of drugs that a physician orders will depend greatly on the type of diabetes an individual has as well as its cause.
Controlling Diabetes
- Lifestyle changes—obedience to the laws of health
- Nutrition: High fiber diet, low glycaemic index carbs. [Baked potato instead of mashed, whole-wheat pasta instead of white, refined sugars] constant eating of highly glycaemic foods that dump large amounts of sugar into the blood will eventually lead to damage of the pancreas causing type 2 diabetes.
- Limit/avoid:
- All animal products (milk, meat, including chicken & fish) because they do not contain any fiber. Animal milk contains sugar and causes diabetes in young people.
- Junk, fatty, fried, and processed foods, caffeine, soft drinks, alcohol, tea, milk.
- Mixing fruits and vegetables
- Eating in between meals (snacking)
- Overeating
- Sodium Chloride (white table salt)
- Eating and drinking at the same time (drink 30 min before & 2 hrs. after meals).
- Eat plenty of:

Controlling Diabetes - Raw fruits and vegetables
- Add seeds to meals (whole or grounded)
- Chia seeds, flaxseed, sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
- Use genuine sea salt or pink Himalayan salt
- Use Tumeric, ginger, and garlic in food liberally
- Blend/juice the green vegetables for the phytochemicals
- Green smoothie blend—spinach, cucumber, green apple, water.
- Ensure meals have something raw (>51%).
- A great thing to do with high blood sugar is to have a big bowl of green salad with some seeds.
- Whole grains
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Sorghum
- Millet
- Barley
- Brown/Red Rice
- Yellow Maize
- Whole Wheat Pasta/Couscous
- Herbs
- Fenugreek
- Psyllium husk (fiber)
- Aloe Vera
- Ginger
- Turmeric
- Ginseng
- Okra (lady Fingers)
- Ashwagandha (lowers the stress hormone—cortisol)
- Milk thistle (supports liver function).
- Exercise: makes cells more sensitive to insulin
- Water: dilutes blood sugar levels and prevents dehydration
- Sunlight: improves the function of beta cells of the pancreas—the cells that produce insulin.
- Temperance: avoid food and drinks that are predisposing to a diabetic state—sodas, juices, donuts, white rice, and other refined sugars. Quinoa is the best grain
- Air: reduced oxygen levels increase insulin resistance—use snake plants indoors.
- Rest: lack of sleep results in unbalanced body hormones, causing high cortisol and low insulin. Shift work is a concern. Cortisol is supposed to be released 6 am-6 pm; 6 pm-6 am melatonin is to be released. However, during shift work, cortisol is needed to keep on alert and working. If there is stress at work, it is double jeopardy. It is best to be in bed by 10 pm.
- Control stress: stress releases cortisol, which suppresses insulin secretion. We must let go instead of harboring bitterness. Forgiveness not only helps relationships but our health as well.
- Supplements—supplements are for adding to our efforts and to support our bodies in what they are deficient in.
- Supplements include:
- Chromium

Medix Select’s Glucose Reduce – A premium supplement by a premium company! [click on the image for more info] - Alpha-lipoic acid
- Vitamin b1
- Cinnamon
- Magnesium
- Probiotics
- Coenzyme Q10
- Vitamin D
- Zinc
- Vitamin C
- Other Therapies
- Fasting once a week—raw vegetables twice a day
- Walking daily or muscle-strengthening exercises
- Sunbathing—20 min.
- Hydrotherapy [2 cups of Epsom Salt in warm water—soak for 20 min.
Diabetes, if not controlled can be a terrible condition with devastating consequences. For prevention, it is best to follow the laws of health listed above.
The rule to follow: prevention is better than cure!
Please feel free to leave any questions, comments, or concerns below.
Good health!!
This disease has done so much harm and is affecting persons from all walks of life and age. Diabetes can come about because of heredity or poor diet. My former co-worker said he got diabetes by drinking a six-pack of soda each day. I believe that diet and exercise are so important in order to bring this issue under control along with taking doctors’ medication. Thanks so much for sharing.
Norman – you are so correct; diet is a significant contributor to developing diabetes. Soda will definitely contribute to its development as it is precisely what happened to a dear friend of mine. It is a terrible disease that affects every part of the body. We must be careful of what we are putting into our bodies.
Thanks for commenting!
What another great informative article about a very relevant topic. I have never really thought about Diabetes much until recently, I got tested at my doctors, I do not have it but need to start watching my diet and exercise.
My Aunty has recently been diagnosed with type 2 and she has just beaten it through diet and weight loss.
Congratulations to your aunty, Dave. This result proves what can be accomplished through diet, exercise,
and weight loss. I hope she keeps up the excellent work! And you will be wise as well to get ahead of the situation with your diet and exercise program.
Thanks for commenting!