There is a condition that is very common to men as they age, commonly known as BPH. Since this is a fact of aging life, it is good to understand what is BPH about.
What is BPH?
BPH stands for Benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is also called prostate gland enlargement, which is a prevalent condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause difficult urinary symptoms, for example blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can additionally trigger bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems.
The prostate gland functions within the male reproductive system. It is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum and surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder.
The prostate’s main function is to generate the fluid(seminal fluid) that nurtures and moves sperm. For more information on the prostate gland, please see the article, All about the Prostate, on this website.
Enlarged prostate is a widespread circumstance. It affects an estimated 50% of men over age 50.
What is the Cause of BPH?
The cause of prostate enlargement is not known. However, it is believed to be related to hormonal changes as men age. The balance of hormones in the body changes as we get older, and in men, this may cause the prostate gland to grow.
Men produce both testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone, throughout their lives. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in the blood decreases, leaving a higher share of estrogen. Studies have recommended that BPH may occur due to the higher share of estrogen in the prostate contributes to the activity of substances that initiate prostate cells to grow.
Another hypothesis points to dihydrotestosterone
(DHT), a male hormone that contributes to prostate development and growth. Some research has shown that even when testosterone levels in the blood start to decrease, high levels of DHT continue to build up in the prostate. This scenario may allow prostate cells to keep on growing. Scientists have noted that men who do not generate DHT do not acquire BPH.
Diet is another underlying factor linking to BPH. For example, fats trigger the increased formation of testosterone and additional hormones.
What is BPH Symptoms?
When the prostate has become enlarged, it can disturb or even block the bladder. Requiring to urinate frequently is a general symptom of BPH. This timing might be every 1 to 2 hours, primarily at night.
Additional symptoms include:
- Bladder not emptying completely after urinating
- Urgency to urinate
- A weakened flow of urine
- Requiring to stop and begin urinating several times
- Delayed starting to urinate
- Difficulty initiating to urinate
- Requiring to push or strain to urinate
If BPH becomes severe, an individual may not be able to urinate at all. This situation is an emergency that requires treatment immediately.
Who is at Risk for BPH?
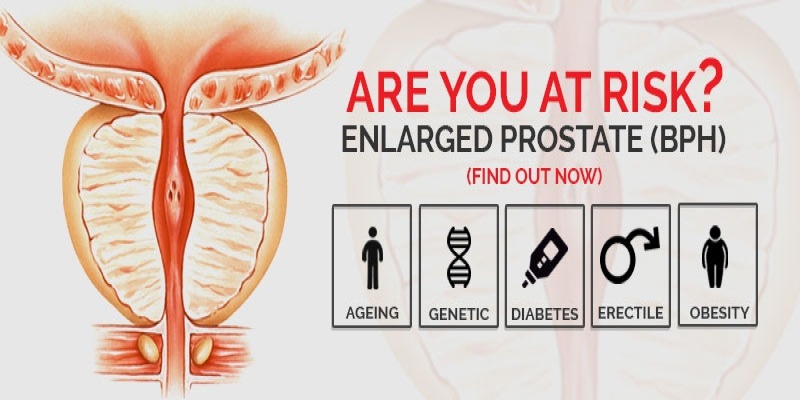
The main risks for BPH are increased age and a family history of BPH. Additionally, lack of exercise, obesity, and erectile dysfunction can also increase the risk.
Treating BPH
Since there is no cure for BPH, the treatment mainly focuses on reducing the symptoms. Therefore, the therapy is based on how severe the symptoms are, how much they affect the patient, and if there are any complications.
Medications
There are several treatment options for BPH. One option available is to take alpha-blockers such as terazosin
(Hytrin) or tamsulosin
(Flomax) to aid in relaxing the prostate and bladder muscles. There is also Alfuzosin HCL ER (Uroxatral).
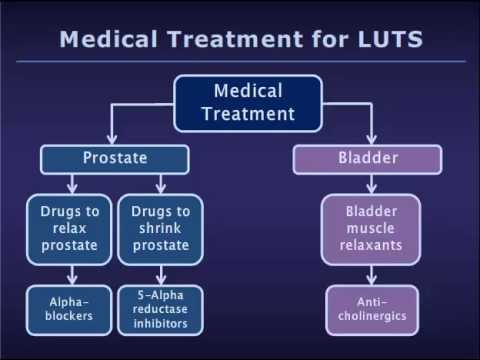
Other drugs available include dutasteride (Avodart) or finasteride (Proscar). These drugs represent a different type of medication for reducing BPH symptoms. These operate by blocking the hormones that trigger the prostate to grow.
A physician may also recommend combinations of these two different types of medications. A physician may also recommend surgery to remove the extra prostate tissue. One standard surgical method for BPH is transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Treating BPH Naturally
There are additional natural therapies that may work to combat BPH symptoms. Conversely, the confirmation on whether these treatments essentially work is debatable. The American Urological Association presently does not propose any herbal therapy for treating BPH.
Individuals who desire to try any of the natural remedies mentioned below should consult their doctor first since some herbal treatments can interact with prescription medications. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not control the value or integrity of herbal supplements. What this means is there can be short of consistent ingredients.
Saw palmetto – Saw palmetto is an herbal remedy that derives from the fruit of a kind of palm tree. It has been used in alternative medicine for centuries to mitigate urinary symptoms, together with those produced by BPH. As per the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a few small-scale studies have suggested that saw palmetto might effectively relieve BPH symptoms.
However, the NIH states that when more extensive studies were performed, it was discovered that saw palmetto was not any more efficient than a placebo. However, research carries on looking into the anti-inflammatory and hormone-blocking properties that saw palmetto might have and its likely use in correlation with other medications. Saw palmetto is trustworthy to use, but small side effects can be upset stomach and headache.
Beta-sitosterol – This herbal medication is a combination derived from different plants that contain cholesterol-like substances called sitosterols or phytosterols (plant-based fats). Several studies have recommended that beta-sitosterol can mitigate the urinary symptoms of BPH, including the strength of urine flow. Additionally, some scientists have suggested that these fatty substances, such as beta-sitosterol, which is found in saw palmetto also, are actually doing the work.
There haven’t been any significant side effects conveyed with the utilization of beta-sitosterol. On the other hand, physicians even now do not know all the long-term effects of this natural therapy.
Pygeum – Pygeum is derived from the bark of the African plum tree and has been utilized in conventional medicine to care for urinary problems since ancient times. It is frequently used to treat BPH symptoms, particularly in Europe. Since studies on Pygeum have not been well-designed, it isn’t easy to determine whether it is effective with certainty.
According to the Canadian Journal of Urology, some small studies have recommended that the supplement can assist with bladder emptying and urine flow. Alternatively, the studies reviewed were lacking consistency. However, Pygeum does appear safe to use, but it may cause headache and upset stomach in some individuals who use it. There are no studies on long-term safety.
Stinging nettle – It is called stinging nettle because the hairs on its leaves can cause severe pain. However, stinging nettle can have some benefits when used as a medicine.
Nettle root is considered to improve a few BPH symptoms and is generally used in Europe. However, a 2007 review concluded that more studies were needed. Currently, there’s no solid scientific evidence to suggest that it’s more effective than no treatment at all.
Sometimes nettle is used in union with other natural BPH treatments, for example, Pygeum or Saw Palmetto. Side effects from nettle are generally mild, including upset stomach and skin rash.
Foods – The effectiveness of diet in the prevention of BPH as well as treating its symptoms continues to be explored.
A recent four-year study in China observed the effects of diet on BPH symptoms. Researchers discovered that men with diets excessive in fruits and vegetables — especially leafy, dark vegetables and tomatoes, had less BPH, fewer symptoms of BPH, and were not likely to have deterioration of their BPH condition. However, the researchers reason that it is not only one nutrient but, more accurately, the combinations found in a healthful diet and lifestyle that are beneficial.
It’s important to note that a supplement is labeled natural does not necessarily mean that it is safe, healthy, or effective. Again, the FDA does not regulate herbal remedies as it does with prescription and over-the-counter drugs. Therefore no one can be entirely certain that what is listed on the label is contained inside the bottle. For this reason, it is essential to obtain supplements from a reputable company.
Additionally, herbal therapies can also cause side effects as well as interact with other medications one might consume. Therefore, a patient should consult with their doctor before trying any natural supplement.
Conclusion
BPH can lead to severe complications if not treated, such as a sudden inability to urinate (urinary retention). An individual may need to have a tube (catheter) placed into his bladder to drain the urine. Other complications include bladder stones, bladder damage, kidney damage, and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Individuals with this condition should monitor it carefully with their physician.
Any questions, comments, concerns, or experiences to share regarding BPH are welcomed to leave them below. You will receive a response.
Good Health!!

 dehydration. This condition occurs since vomiting and diarrhea can cause excessive water to be removed from the body.
dehydration. This condition occurs since vomiting and diarrhea can cause excessive water to be removed from the body.