Explaining the endocannabinoid system is becoming more and more relevant these days because of the ever-increasing popularity of cannabis and the compounds CBD and THC. These compounds, particularly CBD, are crucial for the proper functioning of this system. For more information on these compounds, please read the article, All about Hemp Oil on this website
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system, also known as ECS, is a complicated signaling  system on the cellular level discovered in the early 1990s by researchers examining THC, a celebrated cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. Cannabis is the name of a group of three (3) plants with psychoactive properties, known as Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis.
system on the cellular level discovered in the early 1990s by researchers examining THC, a celebrated cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. Cannabis is the name of a group of three (3) plants with psychoactive properties, known as Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis.
What does the Endocannabinoid System do?
Researchers are still trying to fully comprehend the ECS. But thus far, it is known that it plays a role in regulating a range of functions and processes. 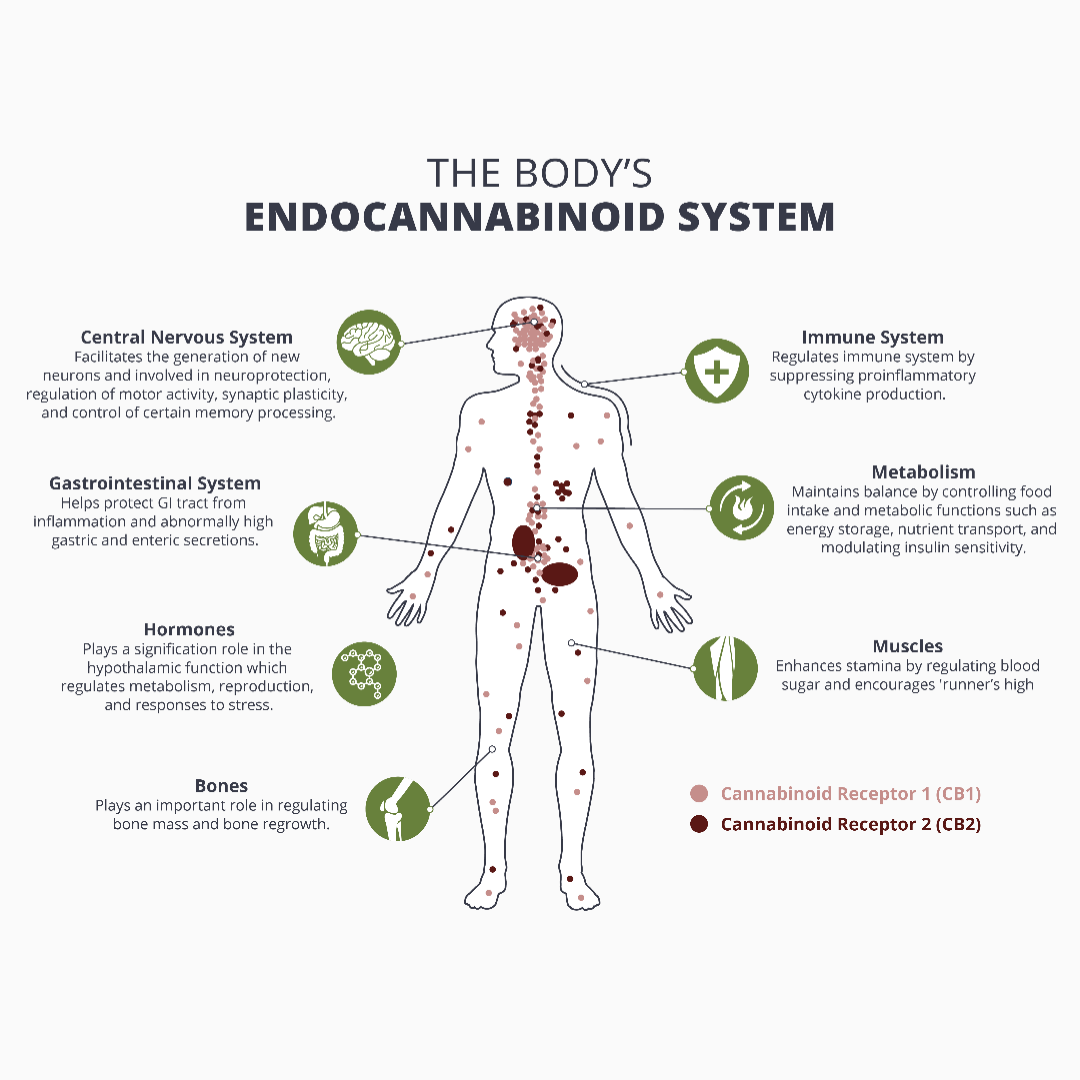 These include appetite, mood, memory, sleep, reproduction and fertility.
These include appetite, mood, memory, sleep, reproduction and fertility.
It is important to note that the endocannabinoid system is alive and active in the body without our use of cannabis.
How does The Endocannabinoid System Work?
The ECS involve three (3) principal components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
First let’s look at endocannabinoids. They are also called endogenous cannabinoids, which are molecules made by the body in the brain. They’re similar to the cannabinoids in the plants, but these are produced by our bodies.
Researchers have recognized two significant endocannabinoids so far:
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
- anandamide (AEA)
These assist in keeping internal bodily tasks running smoothly. The body generates them as needed, making it difficult to know what standard levels apply to each.
Next we have Endocannabinoid receptors. These receptors are located all through the body. Endocannabinoids attach to them in order to indicate that the ECS needs to take action.
There are two (2) principal endocannabinoid receptors:
- CB1 receptors, which are typically established in the central nervous system
- CB2 receptors, which are typically found in the peripheral nervous system, in particular immune cells
Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The resulting effects depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to.
For instance, endocannabinoids might aim for CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in the immune cells to signal that the body is encountering inflammation, which is a common sign of autoimmune disorders.
Lastly, enzymes, those are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they have performed their purpose. There are two (2) principal enzymes responsible for this:
- fatty acid amide hydrolase, that breaks down AEA
- monoacylglycerol acid lipase, that typically breaks down 2-AG
What does the Endocannabinoid System do?
The endocannabinoid system is complicated, and researchers have yet to determine exactly how it functions or all of its prospective functions.
However, Research has linked the ECS to the following processes:
- appetite and digestion
- bone remodeling and growth
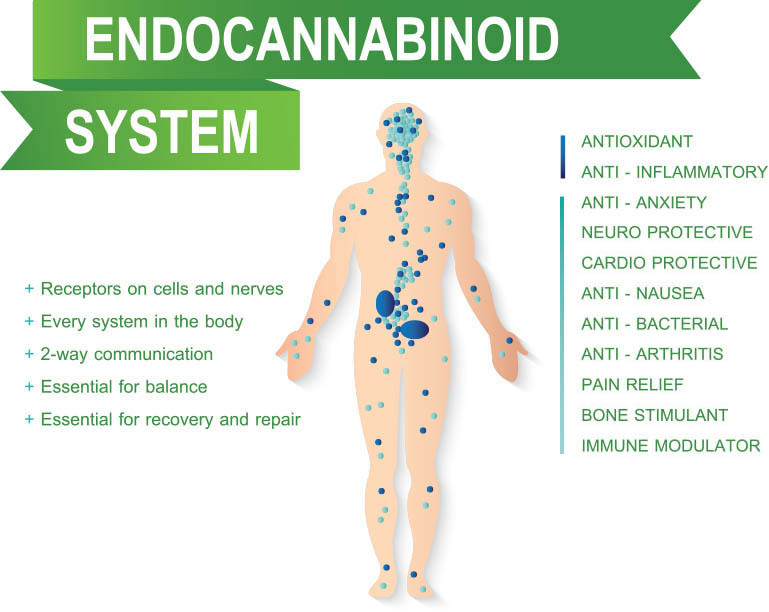
- cardiovascular system function
- chronic pain
- inflammation and other immune system responses
- learning and memory
- liver function
- metabolism
- mood
- motor control
- muscle formation
- reproductive system function
- skin and nerve function
- sleep
- stress
All of these functions contribute to homeostasis, which conveys to stability of the body’s internal environment.
For instance, if an external force, such as pain from a wound or a fever, throws off the body’s homeostasis, the ECS would kick in to help the body return to its normal operative state.
Today, researchers believe that continuing homeostasis is the principal role of the ECS.
How does THC Interrelate with the Endocannabinoid System?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the core cannabinoids found in cannabis. It is the compound that gets an individual “high.”
Once in the body, THC works together with the ECS by attaching to receptors, just like endocannabinoids. It is powerful in part because it can attach to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
This allows it to have an array of effects on the body and mind, a few more pleasing than others. For instance, THC may help to reduce pain and stimulate the appetite. On the other hand, it can additionally cause paranoia and anxiety in some cases.
It is important to note that researchers are currently examining ways to produce synthetic THC cannabinoids that interrelates with the ECS in beneficial ways exclusively.
How does CBD Interrelate with the Endocannabinoid System?
The other core cannabinoid found in cannabis is cannabidiol (CBD). Unlike THC, CBD doesn’t make an individual “high” and more often than not doesn’t cause any negative effects.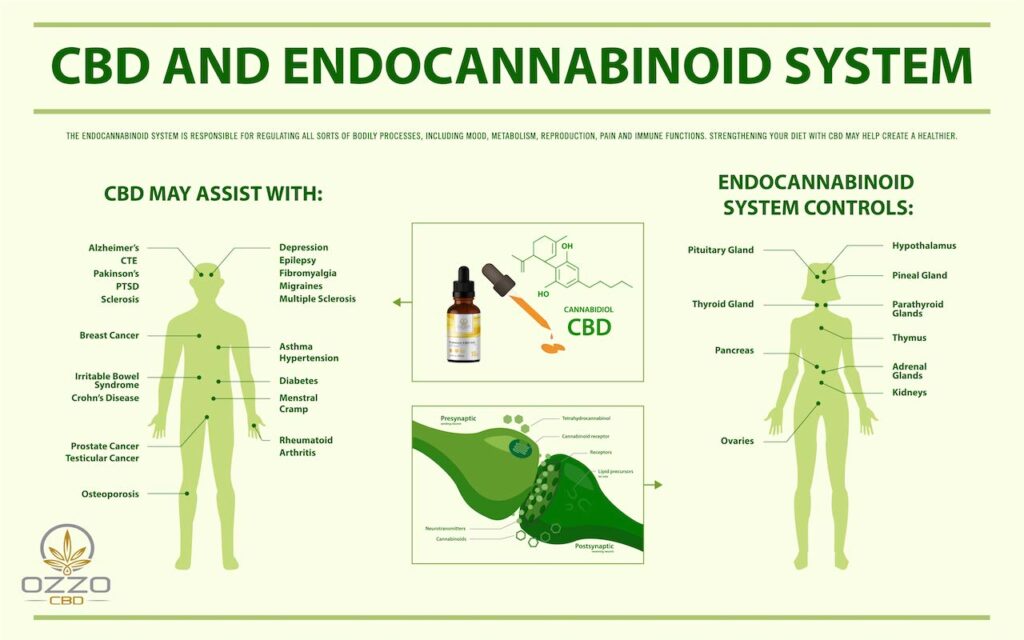
Researchers aren’t totally sure how CBD interrelates with the ECS. But they do know that it doesn’t attach to CB1 or CB2 receptors the way THC does. Instead, a lot of them believe it works by averting endocannabinoids from being broken down. This permits them to have more of an effect on the body. Still, others believe that CBD attaches to a receptor that hasn’t been discovered yet.
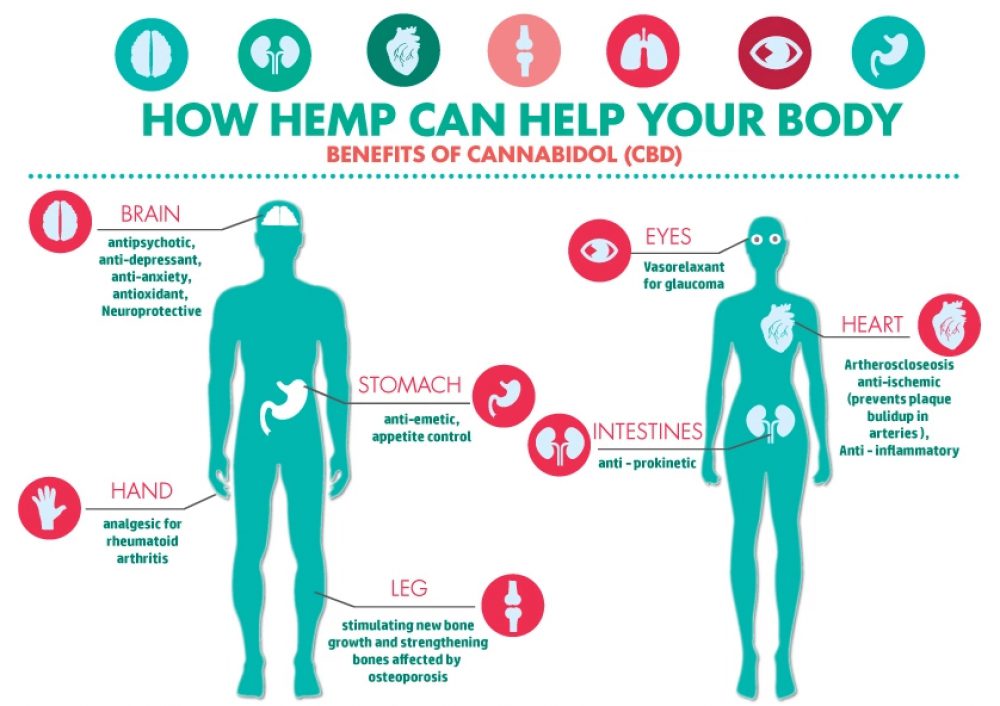
While the particulars of how it functions are still under debate, research indicates that CBD can help with pain, nausea, and other symptoms associated with multiple conditions.
Endocannabinoid deficiency
Some researchers consider a theory known as clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD). This theory advocates that low endocannabinoid levels in the body or ECS dysfunction can contribute to the development of certain conditions.
The theory of clinical endocannabinoid deficiency proposes that in various cases the body doesn’t generate enough endocannabinoids or enough receptors for the endocannabinoid system to perform properly. Consequently, the many functions aren’t regulated properly and the body becomes unbalanced, allowing diseases to arise.
A 2016 article reviewing over 10 years of research on the topic propose that the theory could explain why some people develop migraine, fibromyalgia, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Presently, not any of these conditions has a clear underlying cause. They are additionally frequently opposing to treatment and occasionally appear alongside each other.
If it is confirmed that CECD does play any kind of role in these conditions, targeting the ECS or endocannabinoid production could be the missing key to treatment.
Supplementation
Supplementing the ECS can be a sure way to ensure that your body has enough cannabinoids. One of the ways of accomplishing this is with a high quality hemp oil. Hemp oil contains CBD and has little to no THC which is why it is legal in all of the US and some countries. For FREE samples containing high quality hemp oil CLICK HERE.
Summary
The ECS plays a major role in keeping our internal processes steady and more research is being conducted. As researchers progress in a better understanding of the ECS, it could ultimately hold the solution to treating several medical conditions.
Please feel free to leave any question, comment, or concern below. You will receive a response.
Good Health!!
e
Hi, this is such a great article. The way you explained it is all so simple. It sounds like it could potentially help everybody and almost everything. Also thank you so much for offering free samples. I don’t think I”ve ever seen anyone offer that before. I’ll get some and let you know how they do!
Thanks again!
Great Shaun – I’m glad you enjoyed the article. Enjoy the samples and let me know how you liked them. Thanks for commenting!
Okay, I am VERY glad that I ran into this article. I didn’t know there was this much to cannabis! I’ve learned plenty from his and I appreciate the detail. If you wouldn’t mind answering something for me or linking it to me if you’ve already written about it. Do you think cannabis can also be useful in the industrial world? I know your website specializes in health, but from the looks of this article you seem to know a lot more about cannabis than anyone I’ve ever met, so I figured I’d ask here. If you don’t know, can you give me your opinion?
Thank you for this article! 99% of the content here is new to me haha.
Hello Misael – As a matter of fact there is use for cannabis in the industrial world. It’s called industrial hemp which comes mainly from the stalk of the plants and it has many uses, including textiles, paper, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food, and fuel.It runs parallel with the “Green Future” objectives that are becoming increasingly popular these days.There is also plenty of research being conducted in the medical field for more uses in that category. Hope this helps and thanks for commenting!
Well, this one looks like a very broad part of the body system and I must tell you that I really like the way you have given details about it as well. It’s really nice to learn about how this system actually works out. I didn’t know about the ECS up until now. You know, I also use CBD which it’s primary ingredient is cannabinoid. It seems like this is a researched system in the body.
Hello Payton – Yes the discovery of the ECS is fairly recent and it is still more research being conducted. So stay tuned for more discoveries. I hope the CDB is serving you well. Thanks for commenting!