Temperature – One of the most essential measurements of our existence. But how many of us stop and think about the importance of temperature?
From measuring our air temperature outdoors to making chocolate, temperature is an important factor in our lives.
What is Temperature?
In the most straightforward terms, temperature is an indicator of how hot or cold something is—the measure of hot and cold.
More specifically, it is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object, which is a type of energy associated with motion. The more heat, the faster the particles move. However, how hot is hot and how cold is cold? This is determined by measuring temperature in degrees with an instrument known as a thermometer.
Why is Temperature Important?
Temperature is important because we rely on it for so many aspects of our lives but broadly speaking our comfort and safety. These are numerous, but a few are listed as follows.
Food
Temperature holds significant importance for food manufacturers as well as individuals who are merely looking to cook at home. Whether barbecuing, broiling, frying, or waiting for water to boil, the proper temperature is important in preparing a meal; it affects the quality, flavor, and freshness of food.
Proper temperature is crucial for both the storage and cooking of food. Temperature is a major factor that controls the formation of bacteria (microorganisms) in food.
For safety, fresh foods must be held at suitable cold temperatures to restrain bacterial growth or cooked to temperatures high enough to kill harmful microorganisms.
This applies especially to meat, poultry, and egg products. Therefore, it is essential to use a food thermometer to prevent undercooking, and as a result, prevent food borne illness. These illnesses include Salmonella, Campylobacter, E. coli O157:H7, and Listeria monocytogenes.
For storage, use an appliance thermometer to be sure the temperature of the refrigerator is constantly 40 °F (4.4 °C) or below and the freezer temperature maintains 0 °F (-17.8 °C) or below.
For more information on cooking meat, read the article, The Healthiest way to Cook Meat on this website.
Beverage
In beer and winemaking, temperature plays a major role in the quality of the final product. Atmospheric temperature alone could have a positive or negative effect during the winemaking or brewing process, as well as the temperature at which fermentation takes place.
In milk pasteurization, the temperature is essential for ensuring the removal of the harmful pathogens listed above (i.e. Listeria, Salmonella, and Escherichia commonly known bacteria, E. coli).
Agriculture
In agricultural and greenhouse applications, the temperature can be the variation between life and death for food, plants, and other cultivated products. Should a greenhouse produce too much heat, plants can become stressed or even die
As the fall temperature gradually changes downward, it is essential to remember the important effect that temperature has not only on our health but also on the quality of foods and beverages we make and consume.
Medical-Medicine
Temperature plays a crucial role in medical care for both humans and animals. Our overall health is often reliant upon the correct temperature in many ways as well.
Maintaining proper temperature levels in medical cold storage areas is vital. Incorrect temperatures can negate the medications or vaccines kept in medical refrigerators. Excess temperatures and high humidity are the two most crucial factors in drug deficiency. When subjected to these conditions, the medications can weaken. Furthermore, medical institutions can face fines and or penalties if their medical refrigerators are not performing properly as this poses a health hazard.
The CDC (center for disease control) carried out a study that addressed the improper storage and handling of vaccines. Unfortunately, 76 percent of the chosen 45 providers in the study had some of their vaccines exposed to temperatures that were not within the required cold chain range for a period-of-time. This study prompted the CDC to make changes and illuminations in guidance and requirements for vaccine care.
Health
An important barometer for health is body temperature. What we know as body temperature is the average temperature of the human body. In humans, this average temperature is estimated at around 97 to 99F or 37°C, although this can vary depending on the time of day. This is measured with a body thermometer.
Body heat is generated by the normal metabolic processes that occur within the body. The majority of our body heat is created in organs, for example, the liver, brain, and heart. Additionally, the muscles create a lot of heat, especially when they are active. The hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system continuously adjust the complex activities in the body so the body temperature is generally near the normal range.
When the body temperature rises above the normal range, this is usually an indication of a fever caused by some kind of inflammation. This is an indication of the body’s defense system taking action.
A fever is a reaction to a specific-disease stimuli. The body regulates its temperature to support the body’s own defense mechanisms. Fever is the most widespread form of a disease-related (pathological) increase in body temperature.
When the body temperature lowers below the range (below 95F), it is indicative of a condition known as hypothermia and is a medical emergency.
Measuring body temperature is very crucial in medicine. A number of diseases are recognized by a change in body temperature. With other illnesses, the track of the disease can be monitored by measuring body temperature. This allows the physician to analyze the efficiency of treatments based on body temperatures.
Temperature is crucial, as it is something we feel. Adjustments have to be made to our housing and clothing to it if we live in different places or at different times of the year. If we get too cold or too hot, survival is impossible. However, the heat from the sun also evaporates water
from the ground and drives the water cycle. Water is a necessity.
The Environment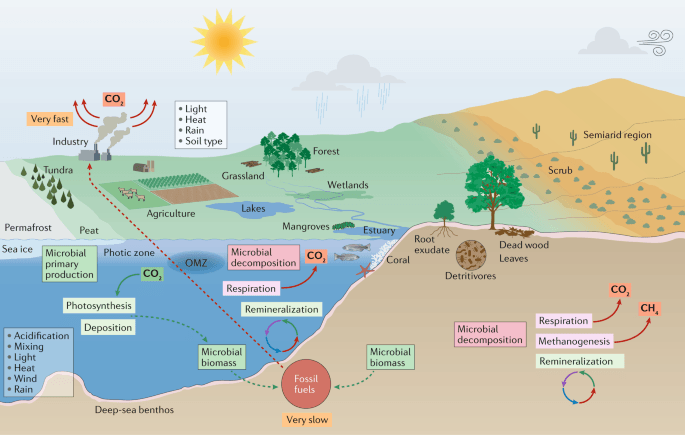
Temperature is among the most all-encompassing and crucial physical factors in the environment. Elements such as viscosity or fluidity, and changes in conditions from solid to liquid to gas, depend on temperature.
The temperature of the earth has an extraordinary impact on our environment. Our use of greenhouse gases has caused the earth’s temperature to rise. As the Earth warms up, heat waves are becoming more frequent in some places, including the US. Heat waves occur when a region experiences exceedingly high temperatures for a number of days and nights.
Heat waves can be hazardous, and cause such illnesses as heat cramps and heat stroke, or even death.
Warmer temperatures can additionally lead to a chain reaction of other changes around the world. This is because increasing air temperature also affects the oceans, patterns in the weather, snow, and ice, and plants animals, and humans. The warmer it becomes, the harsher the impact is on people, and the environment will be.
Below are the major effects that higher temperatures can have on people and the environment:
- Agriculture
- Energy
- Forests
- Health
- Plants, Animals, and Ecosystems
- Recreation
- Water Supplies
On the other hand, temperatures in the other direction can have a strong impact on the environment as well.
For starters, the average number of deaths ascribed to cold is considerably higher than the number ascribed to heat.
Just as it is with warmer temperatures, colder temperatures long-term can affect a host of life’s necessities.
Transportation
There is a variety of transportation effects due to prolonged cold weather. Diesel engines are stressed and, often fuel gels in extremely cold weather, which has an impact on trucking and rail traffic. Rivers and lakes can freeze, halting barge and ship traffic. Consequent ice jams stress bridges and can close major highways.
Cold temperatures take their toll on vehicle batteries. Shear cold temperatures stress metal bridge structures. Transportation losses for one extreme winter totaled $6.5 billion. That amount would be higher in today’s dollars.
Farming

Cold temperature impacts on agriculture are usually discussed in terms of frost and freeze impacts early or late in the growing seasons. Zero temperatures and duration of extreme cold can have destructive effects on trees and winter crops as well.
Prolonged cold snaps can affect livestock that is not protected from the frigid temperatures. In one winter of 1983-84, a single cold snap around Christmas damaged over $1 billion of the citrus crop in Florida. In Louisiana, 80% of its citrus crop was destroyed. Tennessee lost an estimated $15 million in agriculture losses. Texas additionally encountered hundreds of millions of dollars in crop ruin.
Energy
Energy consumption rises significantly during extremely cold weather. This includes increases in the costs of electricity, fuel oil, and coal.
Water Resources and Infrastructure

Prolonged extreme cold temperatures will cause significant ground freezing problems, especially if there is little snow cover. Buried water pipes can burst and cause massive ice problems and loss of water pressure in metropolitan areas.
This creates an assortment of public health and public safety problems. For example, one case of a broken water main in Denver, Colorado required the total evacuation in sub-zero temperatures of the medically fragile patients of the Veteran’s Hospital. Other similar cases of broken water mains have caused the shutdown of subway systems and financial centers.
Schools are generally closed during extreme cold snaps to protect the safety of children who wait for school buses affecting the education process.
As you can see, temperature has a tremendous impact on our environment and well-being and an extreme in either direction can have a divesting impact on our quality of life. Therefore, we must do all we can to avoid having an adverse effect on our climate.
All questions, comments, and concerns are welcomed below.
Good health!!
 depending on the type and cut of meat.
depending on the type and cut of meat.