The purpose of this article is to explain what sleep is and the importance of sleep for health.
Sleep is an indispensable part of our being. Proper sleep is as essential as diet and exercise. Actually, without sleep there would be no diet and no exercise—we simply couldn’t function—period. All of the systems of the body (there are twelve) rely on sleep for efficient functioning. After reading this article you’ll understand how.
What is sleep
Sleep is supposed be a naturally continual state of mind and body. It involves relatively inhibited sensory activity, altered consciousness, reduced interactions with surroundings, reduced muscle activity and inhibition of nearly all voluntary muscles during rapid eye movement sleep (which will be explained later).
The Importance of sleep for health
Sleep plays an important role in our physical and mental health. Decades earlier, most people thought of sleep as a passive, dormant part of our daily lives when the body simply—shut down. However, today we have an understanding that our brains are extremely active during sleep. Furthermore, sleep affects our daily functioning and our physical and mental health in many ways that are just beginning to be understood. For example, sleep is involved in healing and repair of our heart and blood vessels.
When the body goes into sleep mode, it begins its work like the night shift of a factory. During this time, the healing of damaged cells takes place, the boosting of the immune system, a recovering of the day’s activities (e.g. that tension headache disappears), and as mentioned earlier, recharging of the heart and cardiovascular system. Sleep also balances our appetites by helping to regulate levels of the hormones ghrelin and leptin, which play a role in our feelings of hunger and fullness. So when we haven’t had enough sleep, we may feel the need to eat more, which can lead to weight gain.
The third of our lives that we use sleeping are a far cry from being unproductive and plays an immediate role in how complete, energetic and successful the other two-thirds of our lives can be.
These vital renewal activities occur during various stages of sleep.
The stages of the sleep cycle
During sleep, we generally pass through five phases of sleep: stages 1, 2, 3, 4, and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. These stages progress during a cycle from stage 1 to REM sleep, then the cycle starts over again with stage 1. A complete sleep cycle takes an average of ninety (90) to one hundred ten (110) minutes, with every stage lasting between five (5) to fifteen (15) minutes. We adults spend nearly fifty % of our total sleep time in stage two (2) sleep, about 20 percent in REM sleep, and the remaining 30 percent in the other stages. Infants, in contrast, spend about half of their sleep time in REM sleep.
Let’s examine these stages a little further:
Stage One Sleep
During stage one, which is light sleep, we drift in and out of sleep and can be awakened easily. Our eyes move particularly slowly and muscle activity slows.
Stage Two Sleep
When we enter stage 2 sleep, we are still in light sleep. However our heart rate slows and our body temperature drops. Our eye movements stop and our brain waves become slower, with occasional bursts of rapid waves called sleep spindles (sudden bursts of brain activity). The body is getting ready for deep sleep.
Stage Three, Four & REM Sleep
In stage 3, extremely slow brain waves called delta waves begin to appear, combine with smaller, faster waves.
By stage 4, the brain produces delta waves nearly totally. It is especially hard to wake someone during stages three and four, which together are called deep sleep.
There is no eye movement or muscle activity. People who wake up during deep sleep don’t revise instantly and sometimes feel dazed and disoriented for a few minutes after they wake up. Some kids encounter bedwetting, night terrors, or sleepwalking during deep sleep.
During the deep stages of NREM (non REM) sleep, the body repairs and regrows tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. This is a crucial stage.
As we get older, we sleep more lightly and get less deep sleep. Aging is also linked to shorter time spans of sleep, although studies show that we still need as much sleep as when we were younger.
When we switch into (rapid eye movement) REM sleep, our breathing becomes more rapid, irregular, and shallow, our eyes jerk rapidly in various directions, and our limb muscles become temporarily paralyzed during sleep. Our heart rate increases, our blood pressure rises, and males develop penile erections. When individuals awaken in the course of REM sleep, they often describe bizarre and illogical tales – dreams.
How much sleep do we need
The amount of sleep each person needs depends on a range of factors, including age. Infants for example generally require about 16 hours a day, while teenagers need about 9 hours on average. For most adults, seven to eight hours a sleep session appears to be the most effective quantity of sleep, though some individuals may need as few as five (5) hours or as many as the (10) hours of sleep each day. Women within the initial three months of gestation (pregnancy) usually require more sleep than usual. The amount of sleep a person needs also increases if the individual has been deprived of sleep in previous days. Getting too little sleep creates a sleep debt, which is much like over drawing our bank accounts. Eventually, our bodies can demand that the debt be repaid. We may accidentally oversleep or nod off unexpectedly. We don’t appear to adapt to obtaining less sleep than we have a tendency to need; where as we may have a tendency to get accustomed to a sleep-depriving schedule, our judgment, response time and additional functions continue to be impaired. More on sleep deprivation to follow.
On the other hand, getting too much sleep may not be good for you, according to research. A recent study confirms that individuals sleeping on the far side of eight hours could have a greater cardiovascular related death rate. It further revealed that people who slept more than eight hours and less than four hours each night carry the same risk of dying of coronary heart disease (CHD). Sleep is good, but like I always say: too much of a good thing, is a bad thing!
Sleep deprivation and health
Sleep deprivation is simply the condition of suffering from a lack of sleep. Sleep deprivation can be caused by situations that aren’t due to underlying disease. Examples include stress, school or job requirements, poor social habits, or poor sleeping habits.
We all understand the advantages of sleeping well, and we’ve all experienced the feeling of being refreshed after a good night’s sleep. We also know the feeling of fatigue after a poor night’s sleep. But even though we know this, in our busy culture, many of us are not getting the quality sleep we need to truly receive the health benefits of sleep.
Sleep deprivation is a serious menace in our society. It causes problems not only for the victims of sleep deprivation but others around them.
Many studies present it clear that Sleep Deprivation is dangerous. People who were sleep-deprived was tested by employing a simulating driving machine or by using a hand-eye coordination tests performed as badly as or worse than those that were intoxicated. Sleep deprivation also magnifies alcohol’s effects on the body, therefore a fatigued person who drinks will become much more impaired than someone who is well-rested.
How does sleep deprivation affect others in addition to the victim? Driver fatigue is to blame for a probable one-hundred thousand motor vehicle accidents and fifteen hundred deaths each year, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Since sleepiness is the brain’s final step before falling asleep, driving while sleepy will– and frequently will– cause ruinous circumstances. Caffeine and different stimulants cannot overcome the results of severe sleep deprivation. The National Sleep Foundation says that if an individual is having trouble keeping their eyes targeted, if they can’t stop yawning, or if they can’t remember driving the last few miles, they are in all probability too drowsy to drive safely.
Other ways include irritability which makes others uncomfortable. Lack of productivity – a sleep deprived person cannot function as well as one who isn’t. Reflexes are slower and concentration suffers which lead to inefficiency and difficulty learning new concepts.
Focusing back on the individual, ongoing sleep deficiency is linked to an increased risk of heart disease, kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke.
Obesity: poor sleep is strongly linked to weight gain. People with regular shortened periods of sleep tend to weigh considerably extra than those that get adequate sleep. In fact, shortened sleep durations is one of the strongest risk factors for obesity. The effect of sleep on weight gain is believed to be measured by numerous factors, including hormones and the motivation to exercise.
For one who’s trying to lose weight, getting quality sleep is absolutely crucial.
Mental health problems, such as depression, are strongly linked to poor sleep quality and sleeping disorders. It has been predicted that ninety percent of individuals with depression complain regarding sleep quality.
Poor sleep is even associated with an increased risk of death by suicide (for
more info).
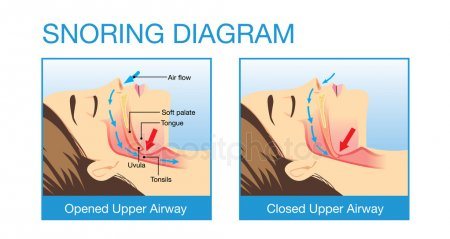
Those with sleeping disorders like insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea additionally report considerably higher rates of depression than those devoid of sleeping issues. For more information on Sleep Apnea, see my article https://universal-health-products.com/sleep-apnea-the-facts/
Sleep will have a significant result on inflammation in your body. In fact, sleep loss is thought to activate undesirable markers of inflammation and cell harm. For more information on cell damage click this link: https://universal-health-products.com/what-are-free-radicals-and-why-are-they-bad/
Poor sleep has been strongly linked to long-term inflammation of the digestive tract, in disorders known as inflammatory bowel diseases (for
more info).
One study discovered that sleep-deprived individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease) were doubly as probably to relapse as patients that slept well. Researchers ar even recommending sleep analysis to help project outcomes in people with long-term inflammatory issues.
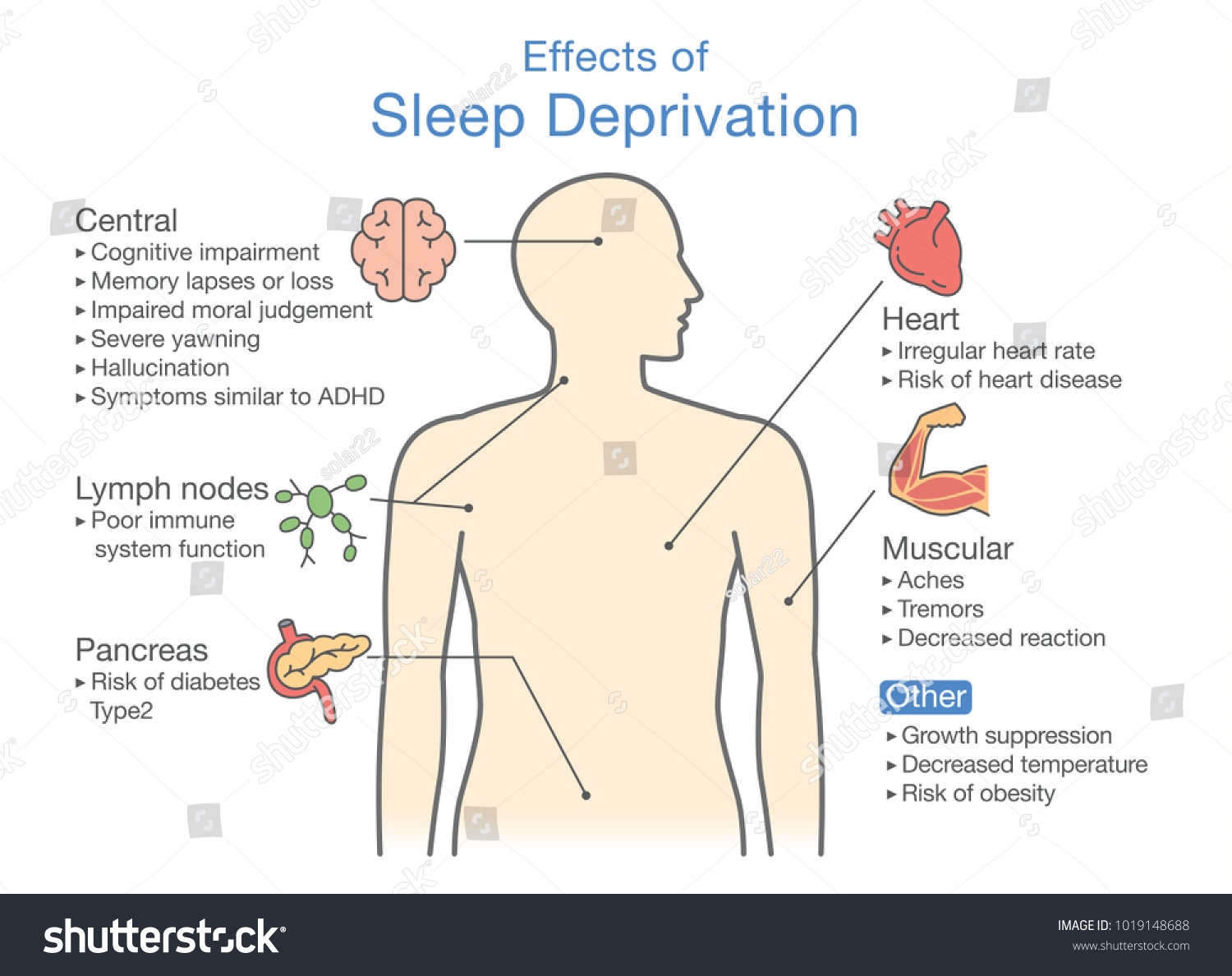
Causes of sleep deprivation
Sleep deprivation can occur for a host of reasons:
- Aging: people 65 and older may have trouble sleeping because of medication they’re taking, or medical problems they’re experiencing and general aging.
- Sleep disorder: these include sleep apnea, insomnia, narcolepsy, and restless legs syndrome.
- Illness. …
- Stress and other factors.
How to treat sleep deprivation
If an underlying medical condition isn’t the cause, there are natural remedies for sleep deprivation. One might try these:
- o Exercise at least 30 minutes per day most days of the week. But not within three (3) hours of bedtime.
- o Get plenty of natural light exposure during the day.
- o Avoid Caffeine late in the day.
- o Avoid heavy consumption of alcohol.
- o Stick to a regular sleep schedule (same bedtime and wake-up time), even on the weekends.
- o Take a warm bath or shower before bed.
- o Establish a regular, relaxing bedtime routine.
- o Take a nap (if possible). While naps don’t essentially structure for inadequate or poor quality nighttime sleep, studies show that a brief nap of 20-30 minutes will facilitate to enhance mood, alertness and performance.
- o Note: keep in mind that getting enough sleep on regular basis is the best way to stay alert and feel your best. But once fatigue sets in, a fast nap will do wonders for your mental and physical stamina.
If there is no change after trying these suggestions, see your clinician.
Please feel free to leave a comment, concern or question below.
Good Health!