Canning foods, a practice for preserving food, was invented in France in 1809 by Nicolas Appert. Although canning has been around for an extended time, the question that appears often is, is it safe? How healthy is canned food? This article looks at these questions and provides the answer.
What is Canning?
Canning is a technique for food preservation in which food is prepared and sealed in an airtight vessel such as a jar or can. An advantage is canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although it can be much longer under specific circumstances.
Canning was first developed in the late 18th century to provide a stable food supply for soldiers and sailors during a war.
The canning method can vary slightly by the processed product, but there are three (3) key steps. These are:
- Processing. The product is first chopped, boned, peeled, sliced, pitted, shelled, or cooked.
- Sealing. Once the food is processed it is then sealed in cans.
- Heating. Cans are heated to destroy dangerous bacteria and prevent spoilage.
This process allows food to be shelf-stable and safe for consumption for 1–5 years or longer.
Common canned foods consist of fruits, vegetables, soups, meats, beans, and seafood.
The Advantages of Canning
Canned foods are convenient, affordable, and have a long shelf life. Additionally, canned foods are an effective and practical way to add increased nutrient-dense foods to a diet.
The availability of safe, quality foods falls short in many parts of the world, and canning aids in ensuring that individuals have a means of access to a wide assortment of foods throughout the year.
Actually, one can find almost any food in a can today.
Additionally, because canned foods can be stored safely for several years and usually involve minimal prep time, they are very convenient.
Furthermore, they are inclined to be less costly than their fresh counterparts are.
How Nutritious are Canned Foods?
Many feel that canned food is not as nutritious as frozen or fresh food. However, that is not always the case. The canning process does not impact fat, carbohydrates, and protein. Fat-soluble vitamins and minerals are additionally not affected. The issue with canning is the excessive heat employed can destroy water-soluble vitamins, like Vitamin B and Vitamin C.
One of the more interesting effects of canning is that a few compounds in food can multiply. Corn and tomatoes are great examples, given that they discharge antioxidants when heated. In general, the nutrients of canned foods are similar to foods preserved through freezing or fresh food.
The Disadvantages of Canning
Canned foods can contain trace amounts of BPA.
BPA (bisphenol-A) is a chemical used in food packaging, including cans, to prevent corrosion.
Studies have shown that the BPA in canned food may migrate from the

can’s lining into the food it encloses.
One study examined seventy-eight (78) canned foods and discovered BPA in over 90% of them. In addition, research has made it apparent that eating canned food is a principal source of BPA exposure.
In one study, contributors who ingested one (1) serving of canned soup every day for five (5) days observed more than a 1,000% increase in BPA levels in their urine.
Even though the confirmation is mixed, some human studies have connected BPA to health issues such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and male sexual dysfunction.
For individuals attempting to reduce their exposure to BPA, consuming an excessive amount of canned goods is not the wisest way.
For individuals that have BPA concerns, the following steps can be taken to reduce exposure:
- Use BPA-free products.
Companies are increasingly producing BPA-free containers. One can look for products labeled as BPA-free. If a product is not marked as such, note that a few, but not all, plastics labeled with recycling code 3 or 7 can contain BPA.
- Avoid the heat.
Do not place plastic containers in the microwave or dishwasher since the heat can cause them to break down over time and permit BPA to seep into foods. - Cut down on cans.
Decrease the use of canned foods. - Use alternatives.
Use stainless steel, porcelain, or glass containers for hot foods and liquids as a replacement for plastic containers.
Additionally, be on the lookout for canned foods containing multiple ingredients, like ready-made soups and pasta, as they often come with higher sodium and sugar levels. They are also some of the most common items too boot.
According to the Canned Food Alliance, canned soups were the most obtained canned item in the United States at 420 million cans in 2018. Further, Americans bought 78.8 million cans of Campbell’s Cream of Mushroom Soup by itself in 2018. Also, note that a single can contains 2,175 mg of sodium. That is almost the entirety of the 2,300 mg recommended sodium intake.
Other canned foods to bypass are vegetables and fruit packed in brine or syrup. A study printed in 2014 in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine discovered that these canned products tend to lose phenolic compounds that make for the flavors, color, and some of the health properties in produce, antioxidants, for example. This result was particularly true if they had been peeled or skinned.
Choosing canned fruits and vegetables that are do not contain these liquids will assist in avoiding this loss. Instead, one should go for products that are packed in water or its natural juice.
Canned foods can contain deadly bacteria.
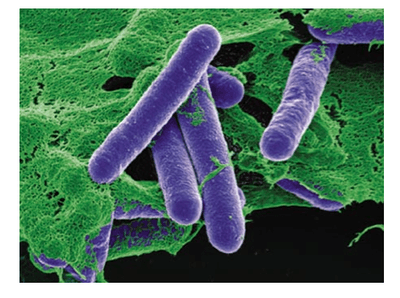
Although it is extremely rare, canned foods that have not been appropriately processed can develop hazardous bacteria known as
Ingesting tainted food can cause botulism, a severe illness that can lead to paralysis and death if left untreated.
Most cases of botulism come from foods that have not been appropriately canned at home. It is important to note that Botulism from commercially canned food is rare.
However, it is important to never eat from dented, cracked, bulging, or leaking cans.
Some canned foods include added sugar, salt, and or preservatives.
Sugar, salt, and preservatives are occasionally added throughout the canning practice.
Some canned foods may have excess salt. Although this does not pose a health threat for the majority of individuals, it may be challenging for others, such as those with high blood pressure.
They can also include added sugar, which can also have harmful effects.
Excess sugar has been linked with an amplified probability of many diseases, including obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. An assortment of additional natural or chemical preservatives may be included as well.
How to Choose the Right Canned Foods
It is wise to study the label on canned foods as well as the list of ingredients, as with all foods,
For individuals concerned about salt, choose the low sodium or no salt added option. Draining the fluid contents from and rinsing foods can additionally lower their salt and sugar contents.
In order to avoid excess sugar, fruits that are canned in water or juice instead of syrup is a viable option.
Some canned foods do not include any added ingredients in any way. However, the only way to know with certainty is to examine the ingredient list.
The Bottom Line
Canned foods can be a viable nutritious option when fresh foods are not accessible, as they provide essential nutrients and are incredibly convenient. Therefore, canned foods can be a part of a healthy diet, but it is critical to read labels and ingredient lists and choose accordingly. Bear in mind, that not all canned foods are created equal.
Also, understand that canned foods are also a considerable source of BPA, which can cause health issues.
Remember the necessity to read the labels.
Questions, comments, concerns, or experiences with canned food are welcomed below.
Good health!!
Your article has made me aware that canned foods can be just as nutritious as fresh and frozen foods because canning preserves many nutrients. I used to think that there is no nutritional value in all canned foods.
I am also happy you managed to address my other worry, which is trying to minimize exposure to BPA. And as with all foods, it’s important to read the label and ingredient list. Great article – Many thanks!
Hi Dave, There are pros and cons to everything it seems and canned foods are no exception. As you say, reading the labels are crucial. They are a tremendous asset.
Thanks for commenting!
I have a question, will it be okay if I eat canned food everyday? I get lazy to cook everyday so I usually find myself eating canned foods. I want to know if there are going to be any side effects in the long run. Also, what canned foods would you suggest that I eat?
I don’t think it’s good to consume anything everyday. Regarding canned foods specifically, the more you consume of them, the more you may be subject to the additives and preservatives they contain, such as BP mentioned in the article. They also tend to contain a good deal of sodium. Fresh food is the best but frozen foods are the closest to fresh, and they can be just as easy for preparation.
I understand that cooking can be a drag sometime, but it’s better for us in the long-run health wise. Perhaps when you cook, cook enough for several servings and freeze the extra to save for future meals to cut the prep time.
You may also try alternating between frozen, canned, and fresh, but try to stay away from canned exclusively.