Oxytocin is one of the “happy hormones.” In fact, it is called the “love  hormone.” Find out why from this article that explores the facts about oxytocin.
hormone.” Find out why from this article that explores the facts about oxytocin.
What is Oxytocin?
Oxytocin is a hormone. Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers made by specialist cells which travel through the bloodstream to tissues and organs, and control most of our body’s major systems. For more on hormones see the article, The Importance of Hormones on this website.
It is produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland. Oxytocin is released when the cells of the neurons in the hypothalamus become excited.
What does Oxytocin do?
Oxytocin is an important hormone in that it plays an essential role in the childbirth process and also helps with male reproduction.
In women, it is liable for signaling contractions of the womb all through labor. Oxytocin engages the uterine muscles to contract, so labor begins. It additionally increases the production of prostaglandins, which move labor along and multiplies the contractions even further. Because of this effect, sometimes synthetic oxytocin (pitocin) is used to cause a woman to start labor if she cannot start naturally, or to make contractions stronger if the labor is slowing.
Once the baby has arrived, oxytocin advances lactation by moving the milk into the breast. When the baby draws at the mother’s breast, oxytocin secretion triggers the milk to release so the baby can feed. Simultaneously,  oxytocin is released into the brain to stimulate further oxytocin production. Once the baby ceases feeding, the production of the hormone terminates until the next feeding.
oxytocin is released into the brain to stimulate further oxytocin production. Once the baby ceases feeding, the production of the hormone terminates until the next feeding.
In men, oxytocin function is less crucial, but it does have a role to play in moving sperm. It additionally appears to affect the making of testosterone in the testes.
Additionally, studies of oxytocin have discovered that it is a crucial chemical messenger that manages some human behaviors and social interaction. It is oxytocin that activates the bond between a mother and an infant, and it may additionally play a role in recognition, sexual arousal, trust, and anxiety. Some research shows that the hormone may even affect addiction and stress also.
The discharge of oxytocin is understood to have a positive effect on family relationships, trust, recognition, anxiety, and sexual arousal. As a result of this, having low levels of the hormone can be detrimental to one’s emotional wellbeing.
The Love Hormone
Oxytocin is sometimes known as the “cuddle hormone” or the “love hormone,” for the reason that it is released when individuals cuddle up or bond socially. Similarly, playing with a dog can cause an oxytocin rush, according to a 2009 study published in the journal Hormones and Behavior.  But there is another side of this coin.
But there is another side of this coin.
Oxytocin can also increase memories of bonding gone bad, for instance in cases where men have poor relationships with their mothers. It can also make individuals less accepting of other individuals they see as outsiders. In other words, whether oxytocin makes one feel cuddly or suspicious of others depends on the environment.
Similarly, with men as with women, oxytocin smoothes the progress of bonding. Fathers who received a boost of oxytocin by means of a nasal spray played more closely with their babies than dads who didn’t get the hormone boost, according to a 2012. Another hormone, called vasopressin, plays a stronger role in men.
Oxytocin Deficiency
Deficiency of the oxytocin hormone is linked to a number of chronic health problems. Below are some signs of low oxytocin levels.
Lack of desire to socialize – Oxytocin is not only known as the “love hormone,” it is additionally referred to it as the “social hormone” because the release of it encourages social interaction. Individuals who are introverted and withdrawn or have social anxiety may additionally have low 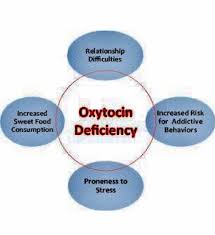 oxytocin levels. According to Autism Speaks, among children with autism, there is a link between low levels of oxytocin and severe social difficulties.
oxytocin levels. According to Autism Speaks, among children with autism, there is a link between low levels of oxytocin and severe social difficulties.
Poor communication skills – Couple interaction and close relationships are linked to oxytocin levels. A study within the journal Biological Psychiatry of forty-seven couples who were given either oxytocin or a placebo administered nasally before an instructed couple conflict session, found that those who received the oxytocin showed increased positive communication behavior in reference to negative behavior.
Low libido –when the brain is experiencing a chemical deficiency, interest in sex declines, it doesn’t seem as enticing as before, and the physical act will leave an individual deficient. As we age, our chemical deficiencies can wane. Having low levels of oxytocin can cause difficulty in one’s sex life with waning desire and performance.
According to an article in The Huffington Post by Eric R. Braverman, MD, the founder father of PATH Medical, women who are deficient in oxytocin may have difficulty with sexual arousal and the ability to achieve orgasm.
Craving Sugar – reduced activity in the brain’s oxytocin system, which is in charge of making us feel full, can be caused by consuming an excess amount of sugar. When oxytocin cells in the brain are blunted, the body seeks out sweets, thus creating a sugar-craving cycle.
Distrust – Another name for oxytocin is the “trust hormone.” If one is feeling distrustful toward their spouse, friends, or society as a whole, that individual could have low oxytocin levels.
Problems with Oxytocin Production
Men with high levels of oxytocin on occasion develop benign prostatic hyperplasia, or the enlarging of the prostate gland. This consequence can cause urinary complaints. On the other hand, a lack of oxytocin can thwart the milk letdown reflex and make breastfeeding difficult. Low oxytocin levels have also been connected to depression, but using oxytocin to treat mental health issues has not yet been studied adequately.
How to Increase Oxytocin
Naturally

Vitamin D – It’s just good to get outside and get some sunshine. This is how we get vitamin D. Every tissue in our bodies has Vitamin D receptors, together with our brain, therefore an insufficiency can lead to damaging physiological and psychological costs.
Research has shown that oxytocin is directly activated and controlled by Vitamin D. In fact, some researchers additionally believe that autistic children possess low levels of oxytocin likely because they are deficient in Vitamin D.
It is particularly important to get some sunlight in the morning to set their circadian rhythm. But for the most part, individuals just don’t get enough Vitamin D from the sun, and that is why I generally recommend taking a vitamin D supplement or using a Vitamin D lamp.
It has been estimated by researchers that half (50 percent) of the general population is in danger of Vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D also naturally increases dopamine levels in the brain, and being deficient in Vitamin D can make you more anxious and more depressed. For more on dopamine, see the article, Facts about Dopamine on this website.
Vitamin C – is an additional way to optimize and increase the levels of oxytocin.
Researchers have long recognized that Vitamin C is a cofactor in the making of oxytocin, and the synthesis of oxytocin is dependent upon Vitamin C.
One study established that Vitamin C promotes the secretion of oxytocin. And another study found that supplementing with a high dosage of Vitamin C increases the release of oxytocin, which then increases intercourse frequency, improves mood, and decreases stress.
As is commonly known, Vitamin C is established in fruits and vegetables for example green peppers, tomatoes, cauliflower, citrus fruits, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage.
Although getting Vitamin C from fruits and vegetables are an excellent route to take, additionally supplements are available to fulfill this goal.
Magnesium – This is a vital mineral that take part in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Unfortunately, many individuals have a magnesium deficiency today. This is unfortunate as magnesium is absolutely crucial for the suitable functioning of the nervous system and optimal neurotransmitter activity.
Researchers have discovered that the oxytocin receptor requires magnesium to perform properly, and magnesium increases the action of oxytocin at the receptor.
There are a number of things an individual can do to make sure they are getting enough magnesium.
First, make sure to consume magnesium-rich sources of food on a regular basis, including spinach, chard, pumpkin seeds, almonds, avocado, dark chocolate and bananas.
Epsom salt baths are an enormous way to increase the body’s intake of magnesium.
Magnesium supplements are additionally a good way to produce more oxytocin
Besides supporting oxytocin levels, magnesium can additionally naturally increase dopamine, reduce anxiety, and assist one to overcome trauma, withdrawal and addiction. For more information on magnesium, see the article How Important is Magnesium on this website.
Taurine – Taurine is an organic compound found in food, mainly found in animal products and it has a wide variety of health benefits. It can cross the blood-brain barrier, improve mood and produces anti-anxiety effects.
Researchers consider that one of the ways it improves mood and reduces anxiety is by naturally intensifying the discharge of oxytocin in the brain.
Touch – There is significant research indicating that personal can touch quickly increase oxytocin levels in the brain. This includes kissing, sex, and cuddling. But also non-sexual touch such as hugging and shaking hands increases oxytocin as well.
A 10-second hug every day can help boost your immune system, fight infection, increase dopamine, reduce depression, and lessen fatigue.
Therefore, to produce more oxytocin, start hugging people… just wait until after the pandemic is over!
Pets – Animals bring us peace and calm, and it’s because they increase oxytocin levels.
Research has shown that just touching a pet lowers an individual’s blood  pressure and increases their oxytocin levels.
pressure and increases their oxytocin levels.
One study found that oxytocin amounts increased in both humans and dogs after just five (5) minutes of petting. This may explain the emotional connection between humans and dogs.
Even just staring into a dog’s eyes can trigger the release of oxytocin in the brain and increase levels.
Massage – Research has shown that a massage can appreciably boost oxytocin levels and reduce stress hormones.
Music – Music carries a host of benefits. It brings joy, energy, and relaxation. Music is in fact healing and can have a calming effect on the brain by increasing oxytocin levels. This holds true of any kind of music as long as it’s the kind that an individual enjoys.
Yoga – Yoga is a well-known “mind-body” leisure method that increases the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Researchers further believe that it works because it increases oxytocin levels in the brain by stimulating the vagus nerve.
Socialization – Socializing can reduce cortisol (the stress hormone) and stimulate the vagus nerve. But additionally, positive social interactions can also increase oxytocin levels.
Researchers have found that the brain releases more oxytocin during social contact and social bonding, and can actually speed up the healing from disease.
You just can’t beat that human communication factor.
Supplementation
If additionally you wish to use supplements to make sure you’re getting what you need to maintain your oxytocin at optimum levels, The Vitamin Shoppe is an excellent on-line source for your supplemental needs.
Please leave any comment, question, or concern below
Good Health!!
 “happy hormones.” This is because among a host of other functions, it has an influence on mood and sense of well-being. Come along as we look at Serotonin: The Facts.
“happy hormones.” This is because among a host of other functions, it has an influence on mood and sense of well-being. Come along as we look at Serotonin: The Facts.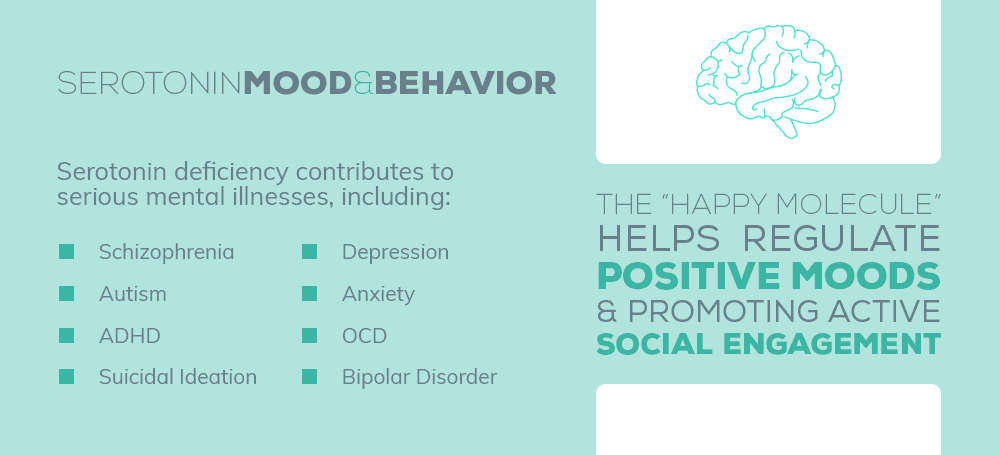
 . However, low levels can contribute to sleep, mood, digestive, and other issues.
. However, low levels can contribute to sleep, mood, digestive, and other issues. starting point for many drugs used to treat clinical depression and other mood disorders.
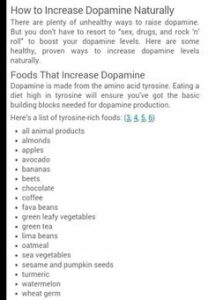
starting point for many drugs used to treat clinical depression and other mood disorders. kidney, pinto, black beans)
kidney, pinto, black beans)
 in the brain to communicate and control movement. In Parkinson’s, one type of neuron steadily degenerates. It doesn’t have a signal to send anymore; as a result the body makes less dopamine. This chemical imbalance causes physical symptoms. These include tremor, stiffness, and slowness of spontaneous movement, poor balance, and poor coordination. Doctors treat these symptoms with medications that raise the levels of this chemical. This consequence on the body’s movement and control can be permanent.
in the brain to communicate and control movement. In Parkinson’s, one type of neuron steadily degenerates. It doesn’t have a signal to send anymore; as a result the body makes less dopamine. This chemical imbalance causes physical symptoms. These include tremor, stiffness, and slowness of spontaneous movement, poor balance, and poor coordination. Doctors treat these symptoms with medications that raise the levels of this chemical. This consequence on the body’s movement and control can be permanent.
 capable of in turn, be the main cause of addictive behavior in our lives.
capable of in turn, be the main cause of addictive behavior in our lives.