We’ve all heard of hormones and one in particular, testosterone. Although we may have heard of it, how much do we really know about testosterone? This article is all about testosterone.
What is testosterone and what does it do
Testosterone belongs to a group of hormones known as androgens which are sex hormones. Testosterone is a hormone found in both male and
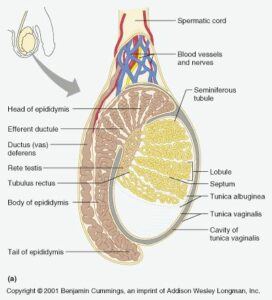
females. However, it is mostly known as the male primary sex hormone as it plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics like increased muscle and bone mass, as well as the growth of body hair. Testosterone is primarily produced by the testicles in men.
In women, produced in small quantities, testosterone is a secondary sex hormone when combined with estrogen, the primary female sex hormone which is produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands, assists with the growth, maintenance, and repair of a
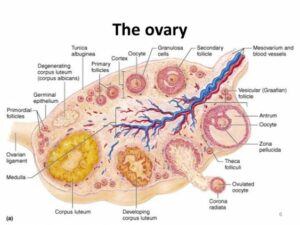
woman’s reproductive tissues, bone mass, and human function. An imbalance of testosterone within the body of a female can have damaging effects on a woman’s health and sex drive.
Men also have estrogen in their systems as a secondary sex hormone Estrogen needs to stay in balance with testosterone to help control sex drive, the ability to have an erection, and the production of sperm.
What are the causes of low testosterone in men
Even though testosterone production naturally tapers off as a man ages, other issues may cause these hormone levels to drop. Injury to the testicles and cancer therapies such as chemotherapy or radiation can negatively affect testosterone production.
Persistent health conditions and stress can also reduce testosterone production. Some of these include:
- AIDS

Male Reproduction System - kidney disease
- alcoholism
- cirrhosis of the liver
A number of men have a testosterone insufficiency called male hypogonadism. This is a condition in which the body doesn’t produce enough testosterone. It may be caused by problems in the:
- testicles
- hypothalamus
- pituitary gland
Men at risk for this condition include those who have had an injury to the testicles. If an individual has gone through chemotherapy or radiation therapy (as mentioned earlier), or had undecended testicles as an infant, he is also considered at risk for hypogonadism.
Symptoms of male hypogonadism in adulthood include:
- erectile dysfunction
- decrease in muscle mass
- infertility
- loss of bone mass (osteoporosis)
- decrease in beard and body hair growth
- development of breast tissue
- fatigue
- difficulty concentrating
- decreased sex drive
For an individual who doesn’t have hypogonadism, but are interested in feeling more energetic and youthful, the following alternative methods may help increase testosterone levels without the use of hormone therapy.
- Sustain a healthy weight. Overweight men are more likely to possess low testosterone levels. Losing weight can bring testosterone levels to normal.
- Regular Exercise. Men that are sedentary tend to have reduced levels of testosterone, as the body doesn’t need as much. Weightlifting can increase testosterone production. The key is regularly using muscles and moving the body.
- Get enough rest. Sleep 7 to 8 hours every night. Not enough of sleep affects the hormones in the body.
- Try vitamin D supplements. A 2011 study
of one hundred sixty-five men recommended that supplementing with about 3,300 IUs of vitamin D per day increased testosterone levels. - Get enough zinc. Zinc deficiency in men has been associated with hypogonadism.
- Testosterone supplements. There are natural testosterone supplements the prompt the body to produce testosterone on its own. [Get Links]
- Enjoy the morning Java (coffee). There is some evidence from a 2008 study that caffeine may increase testosterone levels.
- Consume more nuts and beans. They’re rich in D-aspartic acid, which promotes the making of testosterone, consistent with one 2009 study.
What are the effects of low testosterone in men
Low levels of testosterone, also known as low T levels, will produce an assortment of symptoms in men, including: decreased sex drive, less energy, weight gain, depression, moodiness, low self-esteem, less body hair, thinner bones.
Treatment for low testosterone in men
Testosterone levels can be determined with a blood test. There’s a broad range of normal or healthy levels of testosterone circulating in the bloodstream. The normal range of testosterone for men is between 280 and 1,100 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL) for adult males, and between 15 and 70 ng/dL for adult females, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center. Ranges can vary among different labs, Therefore it is important to speak with a physician regarding results.
If an adult male’s testosterone levels are below 300 ng/dL, a doctor may do a workup to determine the cause of low testosterone, according to the American Urological Association.
Low testosterone levels could be a sign of pituitary gland problems. The pituitary gland sends a signaling hormone to the testicles to produce more testosterone. A low T test result in an adult man could mean the pituitary gland isn’t working properly. But a young teen with low testosterone levels might be experiencing delayed puberty.
Reduced testosterone production, a condition referred to as hypogonadism, doesn’t always require treatment.
An individual may be a candidate for testosterone replacement therapy if low T is interfering with health and quality of life. Artificial testosterone can be administered orally, through injections, or with gels or patches on the skin.
Replacement therapy may produce desired results, like greater muscle mass and a stronger sex drive. But the treatment does carry some side effects. These include:
- oily skin
- fluid retention
- testicles shrinking
- limit sperm production
- decrease in sperm production
- contribute to sleep apnea
- enlarge the breasts
- increase the risk of heart disease
Studies
have found no greater risk of prostate cancer with testosterone replacement therapy, but it continues to be a topic of ongoing research.
One study
suggests that there’s a lower risk of aggressive prostate cancers for those on testosterone replacement therapy, but more research is additionally needed.
Research shows little evidence of abnormal or unhealthy psychological changes in men receiving supervised testosterone therapy to treat their low T, according to a 2009 study within the journal of Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management.
What are the causes of low testosterone in women
The two main causes of low testosterone in woman are:
- A reduction within the levels of the hormone as a traditional consequence of menopause and aging.
- A problem with the ovaries or the pituitary or adrenal glands.
Testosterone decreases naturally a female ages. Levels of other hormones, like estrogen, also reduce over time, especially when a female reaches menopause.
Around the time that menopause commence, a female could also be more
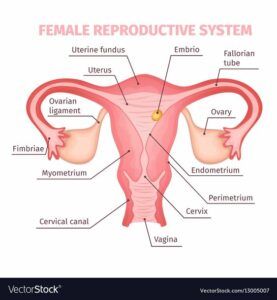
likely to possess less testosterone because the ovaries are producing fewer hormones. Also, medicines that treat the side effects of menopause can lower testosterone levels. One such medicine is oral estrogen.
Issues with the ovaries and adrenal glands can additionally cause lower levels of testosterone. A female may have reduced levels if her ovaries are removed, for instance, or if she has adrenal insufficiency, which suggests that the adrenal glands aren’t working properly.
Please note that at this point, there aren’t any conclusive guidelines for what should be considered “low” testosterone levels in women.
What are the effects of low testosterone in women
Low testosterone can cause one or more of the subsequent symptoms in women:
- sleep disturbances
- sluggishness
- decreased sexual satisfaction
- fertility issues
- irregular menstrual cycles
- muscle weakness
- fatigue
- reduced sex drive
- weight gain
- loss of bone density
- vaginal dryness
It is important to point out that research concerning this area is still limited. Because of this, since the symptoms linked to low testosterone are so widespread, a doctor will search for signs of other issues or conditions before making a final diagnosis.
The doctor may initially check for the conditions listed below:
- depression
- anxiety
- chronic stress
- thyroid disease
- transition to menopause
Treatment for low testosterone in women
SOME estrogen replacement drugs contain testosterone.
However, the quantity of testosterone contained in the drugs might not be enough to boost levels, or the body might not be ready to absorb them adequately.
A doctor can dispense testosterone injections or pellets, expecting these treatments to possess an equivalent effect on women as on men such as: raising energy levels, decreasing fatigue, and increasing the sex drive.
However, many doctors advise women to not take testosterone. Likewise, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have approved only a small number of testosterone-based treatments for ladies. This is often because the side effects can include:
- hair loss
- acne
- excess facial hair
- a deepening voice
- an enlarged clitoris
The 2014 task force advised against treating low testosterone levels in women because of a scarcity of research. However, they noted as an exception that ladies with a condition called hypoactive desire for sex disorder should receive treatment.
A doctor may as an alternative recommend alternative therapies to treat the symptoms of low testosterone in women. These treatments and lifestyle changes can include:
- sex therapy
- taking steps to manage stress
- getting enough sleep
- eating a healthful diet
- taking over-the-counter dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplements
DHEA is a steroid hormone that is also produced by the adrenal glands. The Endocrine Society advise against routine supplementation with DHEA, however, as researchers have yet to prove that supplementation is safe and efficient in the long term.
The side effects of DHEA supplementation are often almost like those of excess testosterone.
Moderately elevated testosterone levels in men tend to provide few noticeable symptoms. Boys with higher levels of testosterone may begin puberty earlier than usual. Women with higher than normal testosterone may develop masculine features.
If Low T is suspected and the natural methods named above has unsatisfactory results, it’s best to consult a physician and have a test to check sex hormones levels. He or she will then administer the proper treatment.
Please leave any question, comment, or concern below.
Good Health!!
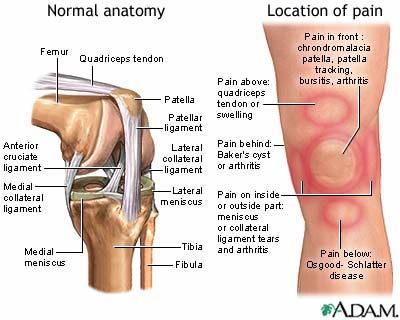
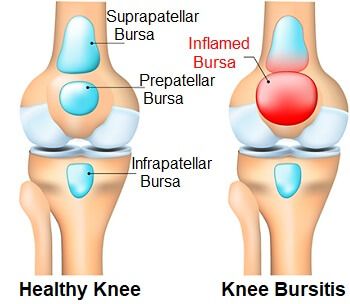 called bursae (bur-SEE) which cushion the bones, tendons and muscles near the joints. Bursitis occurs when bursae grow to be inflamed.
called bursae (bur-SEE) which cushion the bones, tendons and muscles near the joints. Bursitis occurs when bursae grow to be inflamed. pain and tenderness just outside of a joint.
pain and tenderness just outside of a joint.